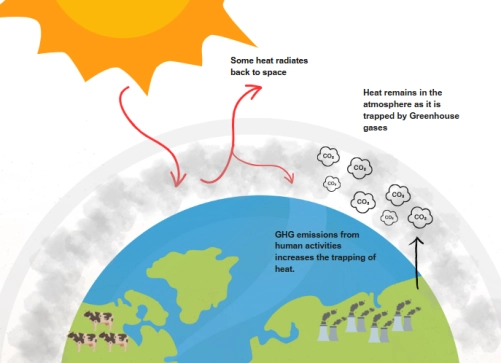
1. How climate change affects companies?
Through their activities and operations, companies contribute to climate change, but climate change may also have negative and positive effects for companies. These negative (respectively positive) effects of climate change are referred to as “climate-related risks” (respectively “climate-related opportunities”) in the Australian Sustainability Reporting Standards (ASRS). Specifically, AASB S2 focuses on climate-related financial risks and opportunities, i.e., climate-related risks and opportunities “that could reasonably be expected to affect the entity’s cash flows, its access to finance or cost of capital over the short, medium or long term.” (AASB S2, para 2).
2. Are all business impacted by climate-related risks?
To different degrees, all companies are likely to be affected by the effects of climate change either directly or indirectly through their supply chain for instance. It is important for companies to carefully identify and assess these risks in order to future-proof their business.
3. Why is climate change so important?
Climate change is so important as it is an intergenerational and international problem and extends right through the future. The consequences of climate change pose a threat to humanity, biodiversity and nature, therefore affecting how we live our day-to-day lives.
4. What can business do about combatting climate change?
Businesses need to perform a carbon footprint assessment to accurately measure their GHG emissions. After establishing this baseline, businesses can then use this initial carbon emissions inventory to identify areas for carbon emissions reduction and develop accordingly a transition plan with emission reduction targets on the short, medium and long term.
5. What is Australia doing about climate change?
Australia turns to the law to try and combat climate change, from a political perspective. Besides establishing legislated emissions reduction target under the Paris Agreement (net zero by 205), Australia is encouraging companies to consider climate change and recently introduced mandatory climate reporting in the hopes to enhance accountability within Australian businesses.
6. What is a climate transition plan?
A climate transition plan or decarbonisation plan is the creation of a step-by-step outline of what the business will do to reduce its carbon emissions and become more sustainable. The plan should include key actions (supported by credible investments) and key milestone.
7. What is climate adaptation?
A climate adaptation refers to the strategy and actions taken by a business to strengthen the climate resilience of its operations, facilities, supply chain… Businesses need first to identify and assess their climate-related risks. Then, they can develop mitigation actions for their material climate-related risks and integrate them in their climate adaptation strategy and policy.
8. Who is responsible for climate change?
While there are much larger polluters in society than others, ultimately climate change an everyone problem. Everyone contributes to the problem, and everyone can make a difference.
How Forvis Mazars can help
- Carbon accounting
- Climate adaptation and transition plans
- Climate risk and opportunity assessment
- Climate scenario analysis
- KPIs audit readiness assessment
Date published: 28/10/2024
Please note that this publication is intended to provide a general summary and should not be relied upon as a substitute for personal advice.
All rights reserved. This publication in whole or in part may not be reproduced, distributed or used in any manner whatsoever without the express prior and written consent of the Forvis Mazars, except for the use of brief quotations in the press, in social media or in another communication tool, as long as Forvis Mazars and the source of the publication are duly mentioned. In all cases, Forvis Mazars’ intellectual property rights are protected and the Forvis Mazars Group shall not be liable for any use of this publication by third parties, either with or without Forvis Mazars’ prior authorisation. Also please note that this publication is intended to provide a general summary and should not be relied upon as a substitute for personal advice. Content is accurate as at the date published.
This website uses cookies.
Some of these cookies are necessary, while others help us analyse our traffic, serve advertising and deliver customised experiences for you.
For more information on the cookies we use, please refer to our Privacy Policy.
This website cannot function properly without these cookies.
Analytical cookies help us enhance our website by collecting information on its usage.
We use marketing cookies to increase the relevancy of our advertising campaigns.